Adherence to stringent food safety protocols isn’t new for those within the food industry. However, the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is a relatively modern framework that has revolutionized these practices, spurred by an increasingly complex and globalized food supply. GFSI is a business-driven initiative led by industry stakeholders to enhance food safety standards, with a core focus on adherence to food safety throughout the supply chain.
GFSI is not merely another regulatory requirement but a vanguard that establishes uniform international standards and catalyzes the harmonization of food safety laws worldwide. Operating as a private organization independent of government agencies, GFSI plays a crucial role in building a mutually accepted certification system within the industry.
In this blog post, I will demonstrate GFSI’s essential role, objectives, and impact on the global food industry.
What is GFSI, and What is it not?
GFSI is not a governmental or regulatory agency but an alliance of industry stakeholders committed to advancing food safety. GFSI was established in 2000 and acts as a collaboration platform, bringing together key players from the food retail, manufacturing, and service sectors, along with international organizations, academia, and regulators. As a coalition of action, GFSI unites diverse organizations, including private companies, industry members, and governmental bodies to achieve common goals such as food safety standards and industry harmonization through multi-stakeholder governance. Within this coalition, industry experts and food safety experts play a key role in developing, overseeing, and verifying GFSI standards and schemes, ensuring trusted food safety management systems globally.
GFSI does not develop or enforce standards and does not issue its own certificates. It benchmarks and recognizes existing food safety certification programs (often called “schemes”) that meet its rigorous criteria. The idea is that a food supplier can get certified to one GFSI-recognized standard and have that certification accepted by major retailers, manufacturers, and food service customers worldwide. This “once certified, accepted everywhere” approach streamlines compliance and avoids the need for multiple audits for different customers.
The Origins of GFSI
The primary impetus for GFSI was addressing recurring food safety incidents and recalls. These events profoundly impacted the food industry’s reputation, consumer trust, and public health. In response to these events, the Consumer Goods Forum (CGF), a global organization of retailers and manufacturers, established GFSI to elevate food safety standards worldwide. The initiative was designed to ensure safe food for people everywhere and to serve the greater good by protecting public health.
What are the Objectives of GFSI?
GFSI chiefly has two main goals:
- To continuously improve food safety management systems.
- To reduce food safety risks by driving the convergence of global standards.
GFSI’s focus on third-party certification is a crucial aspect of its approach, as it assures consumers that food has been produced in compliance with internationally recognized standards.
Let’s break down and explain the objectives of GFSI and the benefits for manufacturers.

Harmonization of Food Safety Standards
GFSI endeavors to standardize food safety practices globally, ensuring that consumers receive the same level of protection irrespective of where food is produced.
This uniformity of standards eliminates the need for multiple audits and certifications, reducing costs and streamlining business processes.
Continuous Improvement
GFSI is committed to continuous improvement in food safety management systems. It provides a benchmarking process that enables schemes to evolve continuously, incorporating emerging scientific knowledge, technological advancements, and industry best practices. The global food safety initiative helps businesses avoid potential food safety risks and adapt to changing regulatory requirements.
Enhancing Consumer Confidence
Businesses should prioritize obtaining GFSI certification to demonstrate their commitment to food safety and quality. Through its benchmarking process and focus on third-party certification, GFSI assures consumers that the food they purchase is safe.
The confidence in their food’s safety directly impacts consumer trust and brand reputation, leading to increased business sales.
Reducing Food Safety Risks
GFSI seeks to identify and reduce global food supply chain risks through its stringent standards and benchmarking process. It enables businesses to mitigate potential risks proactively, preventing foodborne illnesses and recalls by promoting best practices and sharing knowledge.
Improving Food Safety Management Systems
The initiative aims to bolster the capacity of food safety management systems to continually adapt and improve, aligning with evolving science and the well-being of consumers. By promoting a culture of continuous improvement, GFSI creates a more robust and sustainable food supply chain.
What is the Impact of the Global Food Safety Initiative on Food Safety Worldwide?
GFSI’s impact has been far-reaching, both for the industry and consumers. By promoting the harmonization of food safety standards, GFSI has simplified compliance for businesses operating in multiple countries.
This harmonized approach is crucial for ensuring safe food in turbulent times, such as during global disruptions or crises, by providing a resilient and agile framework that helps maintain food safety standards. GFSI’s strategies are especially important in the context of climate change, which introduces new challenges to food safety, pest control, and supply chain resilience, making robust standards essential for food in turbulent times.
GFSI has raised the bar for food safety practices globally and has played a critical role in reducing foodborne illnesses and recalls.
What are Some Common Misconceptions About GFSI?
In working with prospects, we found three main misconceptions about GFSI. Perhaps the most frequent misunderstanding is that it is non-regulatory.
It does not create laws or regulations; instead, it catalyzes the development of private food safety standards.
Another common misconception is that achieving GFSI recognition is a one-size-fits-all solution.
In reality, it offers a framework for continual improvement tailored to the unique elements of a given market and company.
Finally, some assume that GFSI-compliant food is risk-free. However, as with any system, there is still a possibility of food safety incidents occurring.
Why Every Food Business Should Consider GFSI?
1. It streamlines compliance
One of the most compelling reasons businesses adopt GFSI standards is its potential to simplify compliance. With an ever-increasing number of countries adopting GFSI-recognized standards as their regulatory requirements, companies can ensure compliance with multiple jurisdictions by adhering to one set of globally recognized standards. This alignment with GFSI also opens doors to significant business opportunities.
For instance, compliance with GFSI standards enables businesses to fulfill the specialized requirements of major retailers such as Costco. Costco conducts its unique audits for food manufacturing, packing, warehousing, and distribution, which, while customized, are grounded in the benchmarked standards of GFSI. Basically, the Costco audit is GFSI-based.
2. GFSI enhances consumer trust
The significance of consumer trust in the food industry cannot be overstated. By achieving GFSI recognition, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to food safety and provide assurance to consumers that their products meet high standards.

This can increase consumer confidence and loyalty, improving brand reputation and sales.
- It’s a cost-effective solution.
Implementing GFSI standards also has the potential to reduce businesses’ costs. By streamlining compliance and minimizing the risk of food safety incidents, companies can save on recalls, legal fees, and damaged reputation expenses.
- Focuses on improvement
GFSI’s focus on continual improvement means that businesses must continuously evaluate and improve their food safety systems. It leads to a culture of continuous learning and innovation, ultimately resulting in improved processes, products, and overall performance.
- It’s easy to achieve and maintain with technology
The integration of technology in GFSI’s processes has revolutionized food safety globally.
Advanced tools and data analytics streamline benchmarking, ensuring thorough assessments. Blockchain and IoT improve traceability, reducing safety risks and promoting transparency.
GFSI software solutions enhance collaboration and transparency, improve traceability, facilitate document control and audit management, and, finally, streamline the process of compliance with GFSI standards.
How Important is GFSI in the Global Food Industry?
Safeguarding Public Health
Arguably, GFSI’s most critical role is to reduce incidents of foodborne illness through the implementation of its global benchmarked standards, which are far more rigorous and encompassing than many local regulations. This is especially crucial in the face of emerging food safety risks and trends.
Reducing Costs for Businesses
GFSI has reduced costs for businesses operating in multiple countries by promoting harmonization and reducing the need for multiple audits. Additionally, implementing its standards helps companies avoid costly recalls, reputational damage, litigation, and fines associated with non-compliance.
Strengthening Cross-Border Trade
With its focus on global standards and equivalency, GFSI has facilitated trade across borders. By providing a level playing field for businesses, it has eliminated barriers to entry caused by varying food safety regulations in different countries.
Fostering Global Trade
GFSI certification is becoming a de facto standard for the global food trade. It builds trust in the quality and safety of products, streamlines export/import processes, and mitigates compliance risks, thus lowering trade barriers. This has increased collaboration and trade between countries, promoting economic growth and development.

What are GFSI-Certified Standards?
GFSI certifications are not standards but quality stamps indicating that a given food safety management system, scheme, or standard has been recognized as meeting the high bar set by GFSI.
The GFSI certification list is based on international standards and guidelines, providing a consistent framework for benchmarking schemes from different countries.

List of GFSI-Recognized Certification Schemes
The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) recognizes several food safety management schemes that meet its benchmarking requirements. Each scheme addresses various aspects of the food supply chain, from production and processing to packaging and retail.
These schemes are run by independent organizations (“scheme owners”) but are all aligned with GFSI’s core criteria. Importantly, there is no single “GFSI standard” or audit – instead, several standards are GFSI-benchmarked and considered equivalent in terms of meeting GFSI’s food safety expectations.
Below is an overview of some of the major GFSI-recognized certification schemes and what they cover:
- BRC Global Standard for Food Safety: Developed by the British Retail Consortium, this standard covers comprehensive food processing and safety management criteria.
- FSSC 22000: Based on existing ISO standards, it focuses on the certification of food safety systems of food manufacturers.
- SQF Code (Safe Quality Food): The SQF program offers certification for all food supply chain sectors, emphasizing food safety and product quality.
- IFS Food Standard: International Featured Standards (IFS) focus on the safety and quality of processes and products.
- GlobalG.A.P.: Initially focused on good agricultural practices, GlobalG.A.P. has expanded to cover the entire agricultural production chain.
- CanadaGAP: This is a management system designed for companies that produce, handle, and broker fruits and vegetables in Canada.
- PrimusGFS: Used primarily by Americans, the private scheme covers agricultural production, manufacturing, and distribution.
Are GFSI Benchmarked Standards Mandatory for all Food Companies?
GFSI standards are not mandatory but are increasingly becoming a prerequisite for global food trade due to their alignment with international best practices.
Companies can still opt for other standards depending on their needs and market requirements.
However, GFSI certification provides a competitive advantage in the global marketplace. Any retailers and food service providers require their suppliers to be GFSI certified, making it almost essential for companies looking to do business with major players in the industry, such as Walmart, Target, Amazon, or Costco as we mentioned.
To summarize the major schemes, the table below compares key aspects of BRCGS, SQF, FSSC 22000, IFS, and GLOBALG.A.P. – including their typical scope, primary focus, where they’re commonly used, and examples of notable users.
| Certification Scheme | Scope (Where It’s Applied) | Primary Focus (Key Attributes) | Typical Industries Covered | Notable Users / Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRCGS (Brand Reputation Compliance Global Standards) | Food and beverage manufacturing (processing plants); also separate BRCGS standards for packaging production, storage & distribution, etc. | Comprehensive food safety and quality requirements for manufacturers. Highly detailed, with an emphasis on product safety, legal compliance, and consistent quality. Audits can be announced or unannounced to ensure ongoing compliance. | Processed food and drink producers; dairy and meat factories; snack, confectionery, and canned goods manufacturers; packaging suppliers (via BRCGS Packaging); warehousing and distribution companies (via BRCGS S\&D). | Widely used by suppliers to UK/EU retailers (e.g. many Tesco and Aldi suppliers are BRCGS certified). Accepted globally – Walmart and other international retailers also recognize BRCGS certification. Many global food brands use BRCGS at their production sites for its rigorous audit process. |
| SQF (Safe Quality Food) | Farm to fork: Codes for primary production (farms/ranches), food processing facilities, packing houses, bottled beverages, pet food, food packaging manufacturing, and distribution centers. (SQF offers different modules/levels for different parts of the supply chain.) | Food safety management with optional quality components. Strong HACCP-based approach plus management system elements. Focuses on preventing hazards and assuring customers of safe processes. SQF also has an optional Quality Code to certify product quality systems in addition to safety. | Agriculture, food manufacturing, and distribution across all major food sectors. Examples: meat and poultry processing, seafood packing, fresh produce packing, bakeries, dairy processing, dry goods and snacks, beverage processing, food warehouses, etc. Also used by packaging manufacturers for food-grade packaging. | Especially common in North America and Australia, but used worldwide. Retailers and foodservice companies (e.g. Walmart, Costco, Kroger) recognize SQF certification for their suppliers. Thousands of companies globally (14k+ sites) are SQF-certified, including many mid-sized food processors and packers who supply global grocery chains. |
| FSSC 22000 (Food Safety System Certification 22000) | Primarily food processing/manufacturing facilities (including industrial operations like ingredient factories, beverage plants, etc.). Also covers animal feed production, food packaging material manufacturing, and some farm categories (e.g. farming of animals) under specific scope extensions. | ISO-based food safety management – integration of ISO 22000 (management system) with sector-specific prerequisite programs. Emphasizes a systematic, risk-based approach and continuous improvement. Focus is on robust internal systems, documentation, and international standards alignment. Often does not include product quality unless combined with ISO 9001. | Large-scale and multi-site food manufacturers, ingredient and flavor manufacturers, dairy and beverage companies, packaging producers (making food contact materials), and animal feed producers. Favored by companies that already follow ISO management standards or operate globally. Also found in some farming/co-op operations that supply raw materials. | Multinational food and beverage companies and their suppliers. For example, Cargill, Nestlé, Coca-Cola, Mars, Unilever, FrieslandCampina and others have adopted FSSC 22000 in many facilities. It’s also recognized by all major retailers as equivalent to other GFSI certs, so big brands use it to satisfy worldwide customer requirements. Many food ingredient and packaging firms choose FSSC 22000 for its international credibility. |
| IFS (International Featured Standards – Food) | Food processing and packaging of food products (IFS Food standard). Meant for facilities that process foods or pack loose products. Also has variants: IFS Logistics (storage/transport), IFS Broker (agents/brokers trading food), IFS PACsecure (packaging materials). Geared largely toward post-farm gate operations, especially those supplying retailers. | Food safety and quality for retailer-branded supply chains. IFS combines safety, legality, and customer-specific quality compliance. It uses a scoring system (grading non-conformities) rather than simple pass/fail. There’s a strong focus on meeting customer specifications and ensuring product integrity (authenticity, labeling, etc.). Audits are often required to be unannounced by some retailers, to increase rigor. | European food manufacturers across all sectors: e.g. meat processors, bakeries, dairy product plants, frozen and canned food producers, etc., especially if they produce private label goods. Also used by importers and brokers handling food products (via IFS Broker) and cold storage or transport companies (IFS Logistics) in Europe. Growing slowly in North America for firms exporting to EU. | European retail chains and supermarkets are the primary drivers – e.g., Lidl, Aldi, Carrefour, Metro and others mandate IFS for many of their suppliers. Thus, countless suppliers to these retailers (from cheese factories in France to pasta makers in Italy) hold IFS Food certification. Outside retail, some European food brands also use IFS to satisfy their own internal or regional market requirements. The IFS standard is recognized by GFSI, so it’s accepted by international customers similarly to BRCGS or SQF in equivalent situations. |
| GLOBALG.A.P. (Global Good Agricultural Practice) | Primary production (farming and aquaculture). GLOBALG.A.P.’s Integrated Farm Assurance covers crop production (fruits, vegetables, grains, coffee, etc.), livestock rearing (cattle, sheep, poultry), dairy farming, and aquaculture (fish, shrimp, etc.). Separate standards or add-ons exist for areas like compound feed manufacturing, plant propagation material, and Chain of Custody. Focused on the farm pre-processing stage of the supply chain. | Good Agricultural Practices and food safety at the farm level. Emphasizes proper use of chemicals (pesticides, veterinary drugs), hygiene in harvest and handling, environmental sustainability, worker safety, and traceability from field to market. Aims to minimize contamination risks in primary production and assure buyers of responsible farming methods. It’s often updated to include sustainability and animal welfare criteria in addition to core food safety. | Farms, ranches, orchards, greenhouses, fisheries – ranging from smallholders to large commercial farms. Any producer of fresh produce or raw agricultural commodities that will enter the food supply chain can implement GLOBALG.A.P. It’s prevalent in export-oriented fruit and vegetable farms, as well as aquaculture operations. Also used by producer groups and co-ops to certify all their members. | Global produce and aquaculture suppliers to major retailers. For example, virtually all exporters of fruits and vegetables to European supermarkets are GLOBALG.A.P. certified (it’s a common buyer requirement). Large international fruit companies (bananas, pineapples, etc.) use GLOBALG.A.P. for their plantations. In seafood, many fish farms serving markets like the EU or US follow GLOBALG.A.P. standards. With over 190k certified producers worldwide, it includes everything from Kenyan flower farms supplying Tesco to Dutch vegetable growers supplying McDonald’s. Retailers use GLOBALG.A.P. as a baseline assurance for farm-level safety and sustainability before products move into the rest of the supply chain. |
Recognized Certification Program Owners
The backbone of GFSI is its partnership with Certification Program Owners (CPOs), who develop and maintain standards and schemes for benchmarking.
Recognized Certification Program Owners (CPOs) serve as the entities responsible for developing, maintaining, and revising the food safety standards that are subject to GFSI’s benchmarking.
CPOs encompass a variety of organizations, including private-sector companies, non-profit consortiums, and governmental and non-governmental agencies interested in advancing food safety. Some of the CPOs are:
- Food Marketing Institute
- LGC ASSURE
- Foundation FSSC
- FoodPLUS GmbH
- Freshcare
- CanAgPlus
Their standards cover a broad spectrum of the food supply chain, from farming and production to processing, packaging, and retail. CPOs are committed to upholding the integrity and scientific rigor of their standards, ensuring they align with GFSI’s mission to ensure food safety worldwide.
Through their participation in the GFSI benchmarking process, CPOs facilitate a more harmonized approach to managing food safety risks, benefiting stakeholders across the global food industry.
The GFSI Benchmarking Process
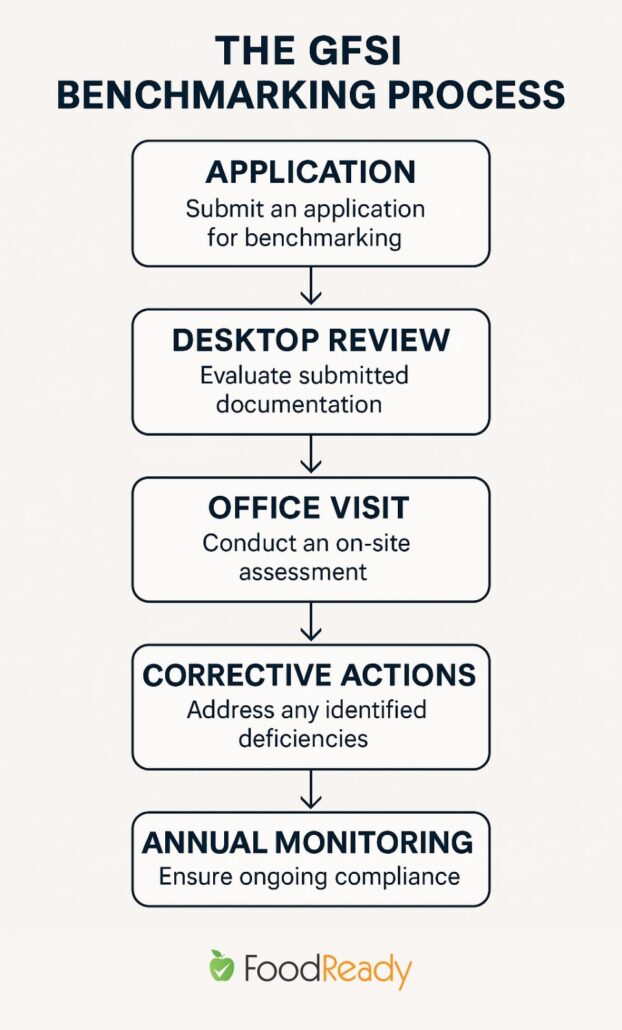
Understanding the Benchmarking Process
The GFSI benchmarking process evaluates food safety management schemes and standards from around the world, ensuring they meet globally accepted food safety criteria. It involves a rigorous review of the scheme’s governance, impartiality, and control measures to ensure its integrity and reliability.
Criteria for Benchmarking
The benchmarking criteria are based on international food safety standards and guidelines, such as those from the Codex Alimentarius Commission and the World Health Organization. These include essential elements like food defense, traceability, allergen management, and product recall procedures. The criteria are continually reviewed and updated to reflect the latest industry trends and best practices.
Benefits of Benchmarking
The benchmarking process offers benefits to all stakeholders in the food industry.
For businesses, it provides a roadmap for improving their food safety management systems while reducing costs. For consumers, it ensures they can trust that their food is safe.
For regulators and governments, it promotes harmonization of global standards, streamlining trade and fostering economic growth.
Continual Improvement Through Surveillance Audits
Once a scheme has been benchmarked, it is subject to regular surveillance audits to ensure its continued compliance with the GFSI criteria. These audits help schemes stay up-to-date with evolving industry practices and technologies, fostering continuous improvement.
Promoting Transparency and Collaboration
The benchmarking process promotes transparency by providing open access to scheme documents and audit reports. It also encourages collaboration between schemes, regulators, and other stakeholders, fostering knowledge-sharing and harmonization of food safety practices. This ultimately benefits the entire global food industry.
How to Obtain a GFSI Certificate?
GFSI certification is obtained through a recognized certification body that audits and confirms compliance with the chosen GFSI benchmarked standard.
The process involves thoroughly evaluating the company’s food safety management system, processes, and documentation.
Once a company is certified, it must maintain compliance and undergo regular surveillance audits to retain its certification.
Organizations seeking to ensure full compliance with GFSI standards may also consider partnering with specialized GFSI consulting firms, such as FoodReady. We provide expert guidance throughout the certification process, helping you to pass the GFSI audit and get GFSI certified.
Read more to learn how we established our food safety system and successfully passed the GFSI audit (SQF) with minimal findings at Munot Plastics.
Ultimately, getting a GFSI certificate demonstrates a company’s commitment to food safety and willingness to adhere to international standards, making it an essential achievement in today’s global food industry.
Stay Globally Competitive with GFSI Certification
FoodReady makes it easy for facilities of any size.
Wrapping-up
GFSI is not merely an acronym in the food industry; it serves as a global superhero for food safety regulations. Rather than a simple checklist, it is a transformative force for prominent food brands. Moreover, it safeguards public health, ensuring that we can enjoy our meals without worry.
GFSI’s future lies in expanding its scope to address emerging issues in the food industry, such as traceability, authenticity, and the role of technology in monitoring and controlling foodborne risks. By continually reviewing and updating its benchmarked standards, GFSI will continue to play a crucial role in promoting food safety on a global scale.
Familiarizing yourself with GFSI could be the key to surviving and excelling in a competitive market.
Finally, remember that ensuring food safety is a shared obligation. By upholding GFSI standards, we can pave the way for a safer and more sustainable future for all.
FAQs
While both GFSI certification and ISO 22000 focus on food safety, GFSI certification involves a benchmarking process that recognizes various food safety management systems that meet its specific criteria, including ISO 22000. However, being GFSI certified means that a certification program has been specifically acknowledged by GFSI, potentially offering broader recognition in the global food industry.
The time to achieve GFSI certification can vary significantly depending on the size of the organization, its current food safety practices, and the specific GFSI-recognized standard it chooses to pursue. Generally, the process can take from a few months to over a year, involving a preparation phase, documentation review, initial audit, and any necessary corrective actions.
Costs for GFSI certification can include application fees, audit fees (which vary depending on the audit’s duration and complexity), and any additional costs related to consulting, training, or implementing necessary changes to meet the certification standards. These investments are often offset by the benefits of improved food safety practices and market opportunities.
Absolutely! GFSI certification is achievable for businesses of all sizes. Small businesses may face unique challenges due to limited resources, but there are specific GFSI-recognized standards that cater to smaller operations. What’s more, there are many resources and tools available to support small businesses through the process.
Some companies may opt out of GFSI certification due to the perceived high costs, the effort required to comply with the standards, or because their customers do not specifically require it. However, even without certification, many businesses still implement food safety practices aligned with GFSI benchmarks to ensure the safety and quality of their products. Understanding these aspects of GFSI certification can empower businesses and individuals in the food industry to make informed decisions about their food safety strategies, contributing to higher-quality and safer food products for consumers globally.






