Food safety hazards can be hidden everywhere and pose significant risks to consumers and food businesses that fail to follow sanitation practices.
Inadequate food sanitation can result in foodborne illness outbreaks, hurting people’s lives and food companies’ reputations. To prevent potential issues, food manufacturers must understand and follow sanitation practices.
In this blog, I’ll explain food sanitation, its importance, key principles, and how digital technology can help streamline food sanitation management in your business.
What Does Food Sanitation Mean?
Food sanitation refers to hygiene and cleanliness practices that food industry professionals implement to reduce the risks of foodborne illnesses. These measures help eliminate conditions that could lead to a food safety hazard, such as contamination from bacteria, viruses, or other harmful substances.
By following food sanitation rules, you ensure that the food you produce doesn’t contain pathogens, foreign objects, or chemical residues, and the consumers will get safe, high-quality food.
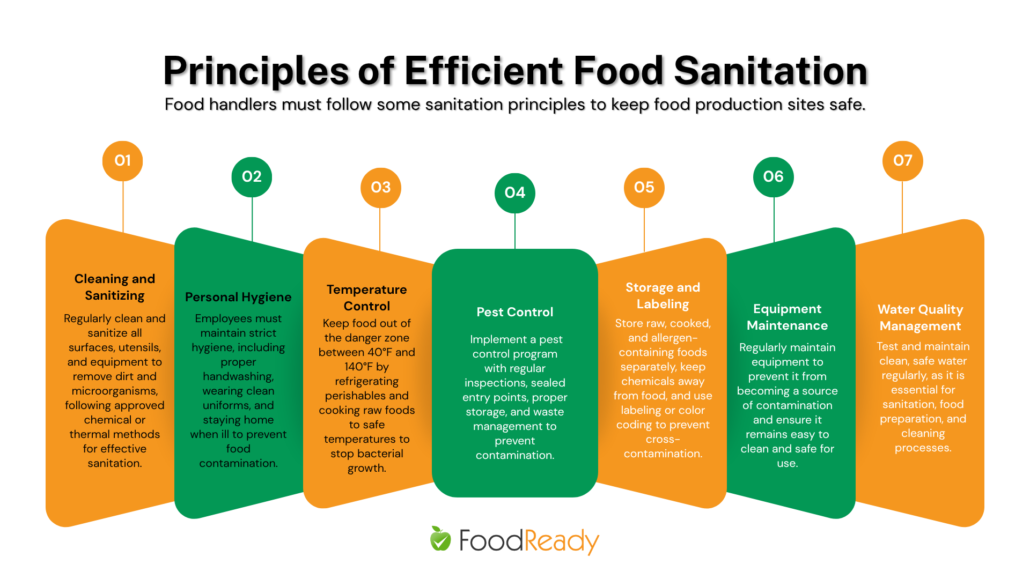
Principles of Efficient Food Sanitation
Food handlers must follow some sanitation principles to keep food production sites safe.
1. Cleaning and Sanitizing
Ensure that the surfaces, utensils, and equipment are regularly cleaned and sanitized to remove dirt, product residue, grease, and microorganisms.
The cleaning involves manually removing dirt and food particles using cloth and rinsing the surfaces. When visually clean, they are sanitized chemically (by approved agents) or thermally (by hot water or steam).
You cannot do vice versa because if there’s still dirt or debris on the surface, it will worsen the quality of the sanitizing process.
The effectiveness of sanitizing will also depend on the sanitizing type, concentration of the chemical agent, contact time with the surface, and other factors. This is why it’s essential to set and follow the guidelines on sanitizing procedures.
2. Personal Hygiene
Personal hygiene is pivotal in ensuring proper sanitation practices. Employees must follow strict hygiene rules to prevent food contamination.
The CDC recommends that workers wash their hands thoroughly with soap and warm water, scrubbing for 20 seconds.
Wearing clean uniforms and hair restraints and avoiding working sick is also necessary, especially if symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, or fever occur.
3. Temperature Control
Keeping food out of the temperature danger zone (TDZ) is non-negotiable. TDZ is the temperature range between 40 °F and 140 °F, where bacteria can double in number in as little as 20 minutes.
Perishable food should be refrigerated under 40 °F, and raw food must be cooked to safe temperatures. Temperature control during storage or transportation is also necessary; thermometers help with this task perfectly.
To support your sanitation efforts, check our guide on best practices for food storage and transportation for actionable insights.
4. Pest Control
Pests are unwanted guests that can pose a serious risk to food safety and sanitary conditions. Pest control plays a key role in maintaining food safety. Implement a comprehensive pest control program, which will include:
- Regular inspections for traces of pests
- Sealing gaps and any potential sources of pests
- Proper food storage organization
- Waste management
Implementing a pest control program will prevent pests from entering the facility and contaminating food.
5. Storage and Labeling
How you store materials is critical when ensuring proper sanitation, and it’s not only about storing foods.
Ensure separate storage areas for raw and cooked foods, allergens, and allergen-free foods to avoid biological contamination and cross-contact. Additionally, chemical agents should be stored far from foods so that there are no chances of chemical contamination.
Waste materials, debris, and leftovers should also be isolated to prevent contamination by biological hazards like pests.
Additionally, labeling will help avoid misusing materials and ingredients like allergens, nuts, or seafood. Use color coding to assign utensils, sanitary equipment, etc., to particular surfaces or foods.
6. Equipment Maintenance
Unmaintained equipment can become a source of biological, chemical, or physical hazards. Poor maintenance can also cause sanitation issues: equipment can become more challenging to clean, deteriorate, and allow bacteria to grow faster inside.
Regular equipment maintenance guarantees cleanliness and a sanitary environment, minimizing contamination risks. This is why equipment maintenance is integral to any food sanitation program.
7. Water Quality Management
Water is used for many indispensable processes, such as sanitation, food preparation, and cleaning, so it must be high-quality and safe. Otherwise, it can become another source of contamination, so regular testing is necessary.
Why Is Food Sanitation Important?
Needless to say, food sanitation is an indispensable aspect of the food manufacturing industry. However, business owners and food handlers must know why it is essential and what can happen if they ignore sanitation principles.
Food sanitation helps ensure food safety.
Following strict sanitation procedures allows businesses to produce safe food without contamination risks. Otherwise, you can end up handling a recall. For instance, a Listeria monocytogenes outbreak at a Boar’s Head plant in Virginia resulted from inadequate sanitation practices. The outbreak led to 10 deaths and 60 hospitalizations.
Maintaining a positive brand reputation.
Outbreak events significantly undermine the reputation of a company accountable for a food safety incident. Consumer trust worsens, and the brand faces regulatory scrutiny, leading to decreased sales, customer loss, fines, and penalties.
Food sanitation is crucial for regulatory compliance.
Food manufacturers must follow regulatory requirements provided by the FDA, USDA, and local departments. Otherwise, they risk getting fines, penalties, or even closing their companies. Adhering to sanitation rules is key to regulatory compliance.
What Are the Compliance Requirements for Food Sanitation?
Regulatory and certification bodies control food sanitation, and complying with the requirements is fundamental for food businesses. Here’s the overview of what regulations food companies must follow:
The FDA and FSMA Requirements
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) oversees food sanitation regulations under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), which obliges food companies to implement proactive sanitation measures as part of their food safety plans.
Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) also establish essential hygiene and operational standards.
USDA Standards
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) mandates meat, poultry, and egg handlers to adhere to stringent sanitation standards. All facilities must have documented Sanitation Standard Operating Procedures (SSOPs).
SSOPs must be regularly validated, reviewed, and implemented consistently. Businesses must also manage daily documentation of all sanitation activities, including CAPA records.
GFSI-benchmarked Schemes
GFSI-recognized programs, such as SQF, BRCGS, or FSSC 22000, require advanced sanitation systems, including documented procedures, risk assessments, employee training, and testing to validate cleaning effectiveness.
These standards help regulate food safety aspects, and food businesses should follow them to safeguard their products, consumer health, and brand reputation in an increasingly scrutinized industry.
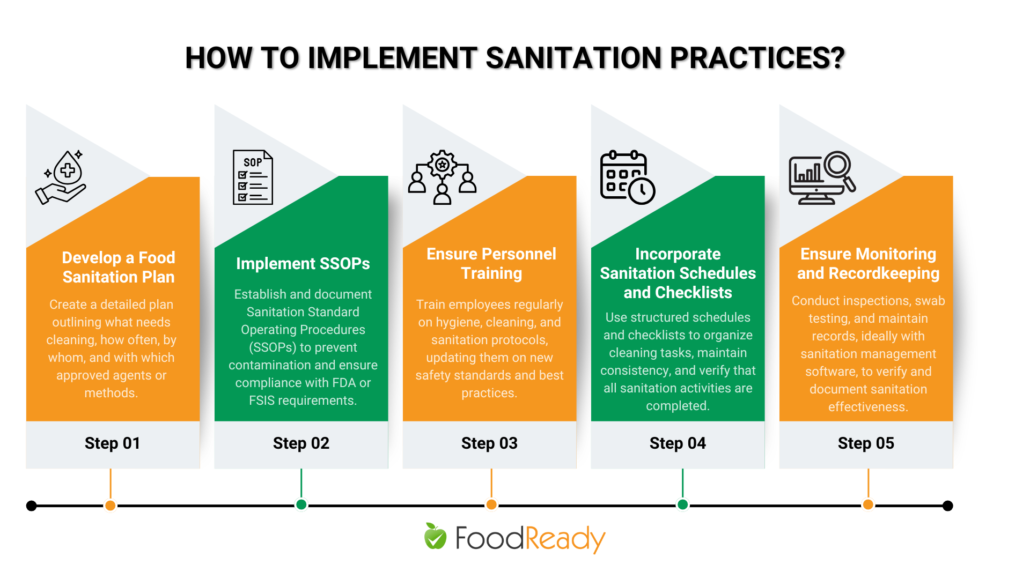
How To Implement Sanitation Practices?
Food businesses must complete several necessary steps to ensure efficient food sanitation. Here are 5 tips to do that.
1. Develop a Food Sanitation Plan
A sanitation plan outlines cleaning and sanitizing procedures in your food manufacturing or processing facility. The plan will cover all areas, including equipment, utensils, and food-contact and non-food-contact surfaces.
In the sanitation plan, you will establish what needs to be cleaned, frequency, responsible personnel, and decide on cleaning agents and step-by-step procedures.
2. Implement SSOPs
Sanitation Standard Operating Procedures (SSOPs) are written procedures that food businesses create and implement to prevent contamination and product adulteration.
You must keep them organized and accessible at the FDA or Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) request.
3. Ensure Personnel Training
Food businesses can’t do without regular worker training. You must educate employees on hygiene and sanitation protocols. Remember that knowledge needs refreshment, so employee education must be consistent to help them keep up with the latest updates.
4. Incorporate Sanitation Schedules and Checklists
You should implement sanitation scheduling to plan daily, weekly, and monthly procedures, ensuring consistency and efficiency. Sanitation checklists will help you track if all the tasks are completed and nothing is missed.
5. Ensure Monitoring and Recordkeeping
Continuous oversight of food sanitation is essential to verifying that your sanitation strategies work. You can perform regular inspections and swab testing. Remember to keep records; food sanitation software can help with this task.
Digital Technologies for Food Sanitation Management
Digital solutions are more than a trend now; they are a multitool that can help you handle sanitation tasks without paperwork. FoodReady sanitation software is the solution that can help you manage food sanitation procedures, from environmental monitoring to audit preparation.
You can customize our digital checklists based on your sanitation procedures, and the dashboards will help you monitor tasks, employees, what steps should be taken, etc. This ensures maximum transparency and prevents sanitation failures before they happen.
If there is a deviation, such as an equipment issue or oversight in cleaning, you can easily implement corrective action. FoodReady ensures you properly fix and document the problem using our document management system.
Our software makes sanitation scheduling more manageable and reliable. You can automate SSOPs and assign tasks to specific employees, ensuring clarity and high performance. You will create an environment where everyone knows what needs to be cleaned and sanitized, how often, and who is responsible.
FoodReady will become your partner in audit preparation! The software enables digital logs of completed checklists, SSOP compliance, CAPA, and verification activities. Instead of wasting time on manual paperwork, you’ll focus on more essential compliance tasks, minimizing stress and improving food safety compliance.
We have helped our customers pass their food safety audits, implement checklists, and significantly save costs, and we will be glad to help you create your success story. Contact us to book a demo and learn more!
Conclusion
Food sanitation refers to hygiene and cleanliness practices that help food manufacturers, processors, distributors, and other food industry professionals maintain food safety and prevent foodborne diseases.
Cleaning and sanitizing, temperature and pest control, proper storage and labeling, and other activities will help achieve the appropriate sanitary environment. To implement these practices, focus on ensuring employee awareness, implement a sanitation plan and SSOPs, and don’t forget sanitation checklists and recordkeeping.
FoodReady can help you manage food sanitation and cover your need for a digital document management system, checklists, SSOPs, regulatory compliance, and more. If you are still searching for a solution, book a demo with FoodReady to learn more details!
FAQs
At first glance, food sanitation and safety can sound similar. However, there’s a difference. Food safety is a broader term, meaning the complex approach to managing food safety risks, while food sanitation is one way to ensure food safety.
Cleaning means removing dirt from surfaces. Sanitizing means killing pathogens at the surface by applying chemicals. Read our blog about cleaning and sanitizing to learn more!
The 5 F’s causing the spread of foodborne illnesses are Food, Fingers, Faeces, Fomites, and Flies.
Food sanitation is a shared responsibility, but the QA team or sanitation manager can typically oversee it.
Cleaning and sanitation must be done as often as necessary. Typical frequency can be before and after each use, between handling raw and ready-to-eat foods, and at established regular intervals during prolonged operations.








