I was fascinated when I heard about the Internet of Things 3 years ago.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has steadily transformed how we interact with the world around us, reshaping industries with its innovative capabilities. In essence, IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity which enables these objects to connect and exchange data.
This interconnected web of devices is revolutionizing industries, and the food sector is a prime example of its transformative impact.
IoT’s core lies in its ability to seamlessly collect and transmit data from various sources. In a world where data is king, IoT provides an unprecedented level of insight and control. For instance, a sensor in a farm can measure soil moisture and temperature, transmitting this data to a farmer’s smartphone, enabling informed decisions about irrigation and planting.
Other devices, such as smart packaging and environmental monitors, are also integral parts of the IoT ecosystem, expanding its reach and functionality.
This real-time data collection and analysis are fundamental to IoT’s value proposition, as IoT devices collect real time data throughout the food supply chain, offering a level of detail and control previously unattainable.
In the context of the Internet of Things (IoT) for food safety, the potential is vast and multifaceted. Food safety involves ensuring that food products are free from contaminants and safe for consumption from production to plate. Traditional methods of monitoring food safety have relied on manual inspections and random sampling, processes that are both time-consuming and prone to human error.
IoT introduces a more systematic, accurate, and efficient approach to this critical area. By employing a network of sensors and devices throughout the food supply chain, it’s possible to continuously monitor various parameters that contribute to food safety, such as temperature, humidity, and even the presence of contaminants.
The integration of IoT in food safety not only promises enhanced monitoring and compliance but also ushers in a new era of accountability and transparency in the food industry. As we explore the role of IoT in food safety, it’s essential to understand its basics, the benefits it brings, the challenges it faces, and the future it holds in transforming food safety standards globally.
Trace Every Detail. Monitor Every Shift.
Explore the software tools that help implement IoT-enabled traceability, cold chain control, and predictive maintenance. All in one dashboard. Gain efficiency while meeting SQF, GFSI, and FSMA expectations.
Key Advantages of IoT Technology in Food Safety
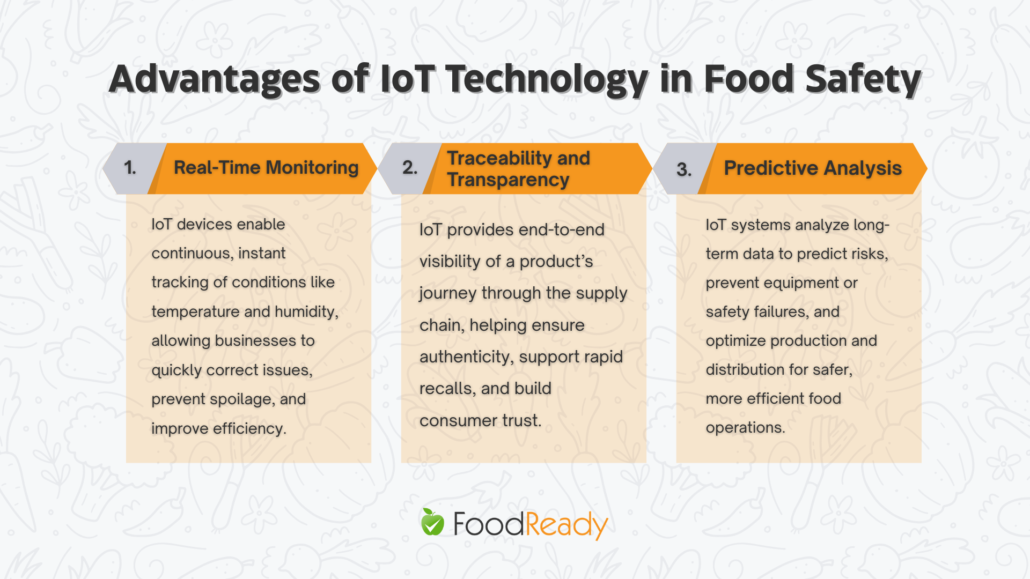
Real-Time Monitoring
The ability of IoT devices to provide real-time monitoring is a cornerstone in maintaining food safety standards. These devices continuously gather data on critical factors such as temperature, humidity, and even the presence of gases, which can indicate spoilage or contamination.
This real-time data is crucial in perishable food items like dairy, meat, and produce, where even a minor fluctuation in environmental conditions can significantly impact their quality and safety. By having constant, real-time updates, businesses can immediately address any deviations from the norm, significantly reducing the risk of spoilage and ensuring that only safe, high-quality products reach consumers.
Furthermore, real-time monitoring facilitated by IoT offers a level of granularity in data collection that was previously unachievable. For example, in a large storage facility, IoT sensors can provide detailed information about different zones, helping to identify specific areas that may require attention or adjustment.
This pinpoint accuracy not only enhances food safety but also optimizes energy use and resource allocation, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. By leveraging these detailed insights, businesses can create more sustainable and efficient operations, aligning with modern consumer expectations of environmentally conscious practices.
Traceability and Transparency in the Food Supply Chain
IoT’s role in enhancing traceability and transparency in the food supply chain cannot be overstated. With IoT, every step of a food item’s journey can be recorded and made accessible. This transparency is crucial not only for compliance with safety standards but also for building consumer trust.
In an age where consumers are increasingly concerned about the origins and handling of their food, the ability to provide detailed information about the supply chain is a significant competitive advantage. For instance, QR codes linked to IoT data can allow consumers to see the entire history of a product, from the farm where it was produced to the conditions under which it was transported.
A digital identification mark, such as a QR code or microchip placed on food packaging, enables both supply chain actors and consumers to verify product authenticity and helps combat food fraud.
Moreover, the traceability provided by IoT is indispensable in the event of a food safety crisis. In cases of contamination or recalls, being able to quickly and accurately trace the source and distribution path of a product can drastically reduce the scope and scale of the impact.
This rapid response not only protects consumers but also minimizes waste and economic loss. Additionally, the data collected through IoT can be used to identify and address systemic issues within the supply chain, leading to continuous improvements in food safety practices and reducing the likelihood of future incidents.
The organic food industry’s efforts to use digital identification marks on food packaging further demonstrate a commitment to ensuring product authenticity and building consumer trust.
Predictive Analysis
The predictive analysis capability of IoT represents a proactive approach to food safety. By analyzing the data collected over time, IoT systems can identify patterns and predict potential issues before they arise, significantly enhancing quality assurance by ensuring food safety, product traceability, and early detection of contamination or food fraud.
This predictive analysis can range from anticipating equipment failures that could lead to unsafe storage conditions, to identifying areas of the supply chain that are more prone to safety breaches. This early warning system allows businesses to address potential problems before they escalate, ensuring the consistent quality and safety of food products.
In addition to preventing foodborne illnesses, predictive analysis through IoT can also optimize the food supply chain. By predicting demand and potential supply chain disruptions, businesses can better plan their production, storage, and distribution, reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
This aspect of IoT not only contributes to food safety but also to the overall sustainability of the food industry. In a world facing increasing challenges related to food security and environmental sustainability, the role of IoT in enabling smarter, safer, and more efficient food production and distribution is invaluable.
IoT Applications in Food Manufacturing and Food Processing
IoT applications are reshaping food manufacturing and processing by delivering actionable insights and automation across the supply chain.
IoT sensors can monitor temperature, humidity, and other critical environmental factors to ensure that food products are stored and transported under optimal conditions, reducing the risk of spoilage and contamination.
These smart devices also enable food manufacturers to track customer behavior, monitor inventory levels, and optimize supply chains for greater efficiency.
Beyond environmental monitoring, IoT technologies can predict maintenance needs for equipment, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth operations. By analyzing IoT data, food manufacturers can identify trends, detect anomalies, and make data-driven decisions that enhance food quality and safety.
The ability to monitor temperature and track customer behavior in real time allows businesses to remain competitive, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency. Ultimately, IoT solutions empower food manufacturers to adapt quickly to market trends and deliver consistently high-quality products.
Case Studies of Successful IoT Implementation in Food Safety
Case Study 1: Real-Time Cold-Chain Monitoring in Delivery Vans
A major grocery distributor in Ireland equipped three of its delivery vans with LTE-M IoT sensors monitoring temperature and vehicle movement in real time; the system triggered alerts when the cold chain was at risk, significantly reducing food spoilage and enhancing food safety compliance.
Why it matters: This shows how deploying IoT in logistics ensures refrigerated goods remain within safe temperature ranges during transit, reducing risk of contamination and meeting regulatory demands.
Case Study 2: IoT for End-to-End Traceability in the Food Supply Chain
A food logistics research team designed and tested an IoT traceability system that used multi-sensor devices, monitoring temperature, humidity, oxygen, light, and GPS location, to track perishable foods from source to distribution in real time; data were transmitted via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, giving operators continuous visibility into product safety conditions.
Why it matters: This demonstrates how multi-point IoT monitoring strengthens traceability, improves safety during storage and transport, and ensures perishable foods remain within safe environmental thresholds throughout the supply chain.
Optimizing Food Processing with IoT Applications
IoT applications are driving significant improvements in food processing by delivering real-time data on processing conditions, equipment performance, and product quality.
IoT sensors monitor temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors to ensure that food processing occurs under ideal conditions, reducing the risk of food safety incidents. These connected devices also track energy usage and monitor equipment performance, enabling predictive maintenance that minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of critical assets.
By harnessing IoT data, food manufacturers can optimize processing conditions, reduce energy consumption, and enhance product quality. IoT solutions also help streamline logistics processes, reduce manual processes, and improve operational efficiency across the board.
The result is a more agile and cost-effective food manufacturing operation that prioritizes food safety, quality control, and sustainability.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing IoT for Food Safety
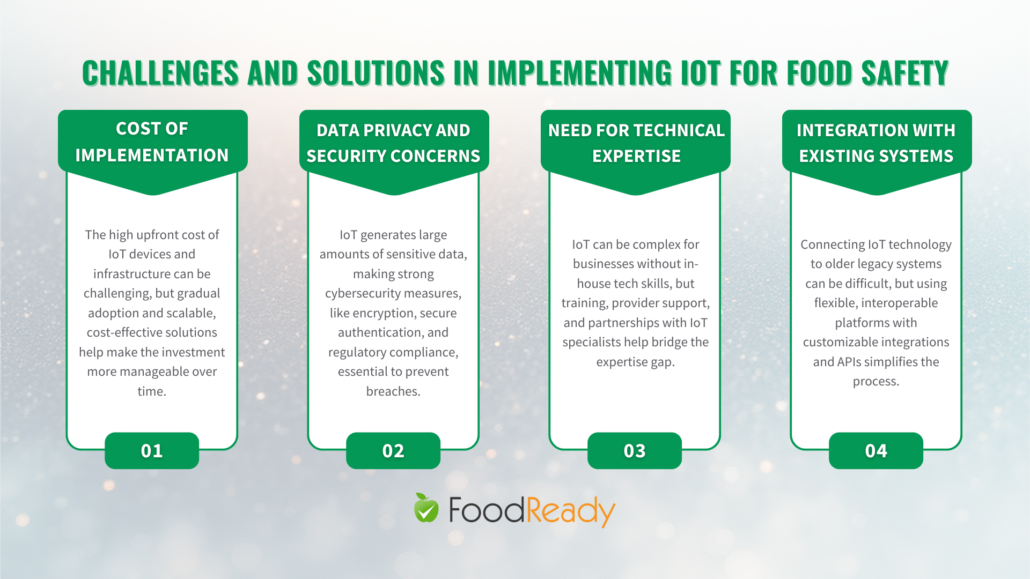
Cost of Implementation
One of the primary challenges in implementing IoT in food safety is the high initial cost. This includes the expense of purchasing IoT devices, setting up the necessary infrastructure, and integrating these technologies into existing systems.
For many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the food industry, this investment can be daunting. However, the solution lies in the gradual adoption of IoT technologies and leveraging cost-effective solutions. Many tech companies now offer scalable IoT solutions that allow businesses to start small and expand their IoT capabilities as they grow.
Additionally, the long-term benefits of IoT, such as reduced waste, improved efficiency, and compliance with safety standards, often offset the initial investment over time.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The vast amount of data collected and transmitted by IoT devices raises significant privacy and security concerns. The risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information is a major challenge for businesses implementing IoT.
To address this, robust cybersecurity measures are essential. Implementing advanced encryption techniques, secure user authentication protocols, and regular security audits can help protect sensitive data. Furthermore, adhering to international data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, ensures compliance and builds trust with consumers who are increasingly concerned about their data privacy.
Need for Technical Expertise
The complexity of IoT technology necessitates a certain level of technical expertise, which can be a barrier for businesses lacking in-house technical skills. This challenge is particularly pronounced in the food industry, where expertise is traditionally more focused on food production and safety rather than advanced technology.
The solution lies in education and training. Many IoT providers offer training programs and support to help businesses effectively use and manage their IoT systems.
Additionally, partnerships with technology firms specializing in IoT can provide the necessary technical support and expertise, allowing food businesses to focus on their core operations while leveraging the benefits of IoT.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating IoT technology with existing systems and processes can be complex and time-consuming. This integration challenge is often due to compatibility issues between new IoT devices and older legacy systems.
The solution involves adopting flexible and interoperable IoT solutions that can easily integrate with a variety of systems. Many IoT platforms now offer customizable options and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that facilitate seamless integration.
Additionally, seeking assistance from IT professionals who specialize in system integration can greatly simplify this process, ensuring a smooth transition to IoT-enhanced operations.
By addressing these challenges with strategic solutions, businesses in the food industry can effectively harness the power of IoT to improve food safety, gain operational efficiencies, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
In conclusion, IoT’s role in food safety is more than just a technological advancement; it’s a commitment to food safety and, therefore, public health.
By embracing IoT, the food industry can ensure higher standards of food quality, reduce wastage, and build greater consumer trust. The future of food safety lies in the smart integration of technology, and IoT is leading the way.
The Future of Food Safety and the Internet of Things
The future of food safety is inextricably linked to the continued adoption of IoT technologies across the entire food supply chain. As the global population grows and consumer expectations evolve, the food industry must ensure that food safety, quality control, and sustainability remain top priorities.
IoT sensors, devices, and systems will play a pivotal role by providing real-time monitoring and data collection, enabling food manufacturers to detect anomalies, predict maintenance needs, and optimize food processing conditions.
With IoT solutions, food manufacturers can more easily comply with food safety regulations, reduce waste, and improve operational efficiency. The ability to collect and analyze IoT data empowers businesses to make informed decisions and continuously improve food safety practices.
As the food industry evolves, leveraging IoT technologies will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge, ensuring food security, and meeting the demands of a growing global population. By embracing the Internet of Things, food manufacturers can build a safer, more transparent, and more sustainable future for the entire food supply chain.
FAQs
IoT enables real-time alerts and data-driven insights, allowing faster response to deviations in safety standards. This rapid intervention can limit the scale of safety breaches, protect consumers, and reduce waste.
Many tech companies offer scalable IoT solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These solutions allow businesses to start with basic features and expand as their operations grow, thus effectively managing costs.
IoT devices can optimize resource use through precise monitoring and control, such as energy and water. This reduces environmental impact and aligns with sustainability goals in food production.
Implementing advanced encryption, secure authentication, and regular security audits are crucial. Adhering to data protection laws like GDPR also helps manage privacy and build consumer trust.
IoT facilitates detailed tracking of food items throughout the supply chain. Information accessible via QR codes can include production details and transportation conditions, increasing transparency and enhancing consumer trust.
By continuously monitoring conditions such as temperature, humidity, and contamination risks, IoT systems detect hazards early. This allows corrective action before unsafe products reach consumers, significantly lowering the chance of outbreaks.
Not entirely. IoT enhances inspections by supplying continuous, real-time data, but regulatory inspections still play a vital role. Together, these approaches create a more robust food safety system.
IoT sensors track refrigeration units and transport conditions minute by minute. They immediately flag any deviation from safe ranges, ensuring perishable foods remain within required temperatures throughout the supply chain.
By providing precise data on storage conditions and equipment performance, IoT minimizes spoilage. Predictive analytics also help optimize inventory and production planning, reducing unnecessary waste.
Yes. Scalable, modular IoT tools allow small businesses to start with affordable monitoring solutions and expand as their operations grow, ensuring food safety compliance without overwhelming costs.
With traceability tools, IoT makes it possible to quickly identify the exact location of compromised products. This targeted approach speeds up recalls, limits product loss, and protects brand reputation.
They track factors like temperature, humidity, pressure, gas presence, equipment health, and even soil or crop conditions. This detailed data builds a full picture of safety and quality from farm to fork.
IoT automates recordkeeping and monitoring, generating audit-ready data logs that align with regulatory requirements. This reduces the burden of manual documentation and ensures more reliable compliance.
Strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular system audits are critical. Protecting sensitive operational and supply chain data is just as important as protecting food itself.
IoT will continue advancing predictive analytics, AI integration, and consumer transparency tools. In the near future, it’s likely that “smart food systems” will become the industry norm, combining safety, efficiency, and sustainability in one ecosystem.







