Food quality management software is a digital system designed to control, monitor, and document the processes that influence product quality across a food operation. It centralizes quality tasks, records, and performance data into one platform, eliminating manual paperwork and reducing errors.
In the food industry, digital transformation is reshaping how companies approach food quality management and how they build a modern quality management system in the food industry. Food QMS platforms are a central part of this shift, driven by changes in regulatory oversight, monitoring expectations, and enforcement practices worldwide.
Manufacturers, processors, and distributors use these systems to standardize quality checks, streamline communication, and maintain real-time visibility across production lines, suppliers, and facility operations. By digitizing workflows, teams can catch deviations faster, document corrective actions accurately, and ensure that quality standards are met consistently across all shifts and locations.
The software also plays a critical role in supporting compliance with industry and regulatory frameworks. Integrated tools help facilities maintain alignment with HACCP plans, GMP requirements, GFSI schemes such as SQF or BRCGS, and evolving regulations including FSMA. This connection between quality management and food safety programs allows businesses to remain audit-ready, reduce risk, and operate more efficiently.
Why Food Companies Need Food Quality Management Software?
Regulatory and Certification Compliance
Food companies operate under strict regulatory oversight, and QMS software helps ensure that every requirement is consistently met. These platforms play a key role in supporting food safety compliance with industry standards by streamlining processes and documentation.
Digital systems support compliance with FDA and USDA regulations, FSMA preventive controls, and documentation requirements for inspections. They also align with major GFSI certification schemes such as SQF, BRCGS, and FSSC 22000 by standardizing records, integrating and documenting prerequisite program controls as foundational elements, and maintaining accurate documentation trails.
A centralized platform keeps all safety records organized and accessible, making it easier to demonstrate compliance, verify process controls, and manage audits. Built-in traceability tools also strengthen the ability to track ingredients, packaging, and finished goods across the supply chain, which is essential for certification and regulatory verification.
Recent industry data reflects this shift toward structured quality systems. A 2025 manufacturing survey reported that 55% of respondents already use a quality management software to manage quality processes, driven by goals such as increased compliance, reduced costs, and reduced risk.
This underscores why digital QMS platforms have become a core part of compliance strategy rather than a nice-to-have.
Strengthen Compliance From Day One
Customize the digital solution to
your exact business operations
Product Consistency and Quality Control
Food quality management software reduces variation by enforcing standardized procedures, including standard operating procedures, and quality checks across every shift and facility. The software ensures that operators consistently follow SOPs, which helps maintain uniformity and compliance.
Digital forms ensure that operators follow the same criteria for inspections, testing, and approvals, regardless of who performs the task. Quality policies are integrated into the framework, supporting consistent product quality and regulatory adherence. This consistency helps maintain product specifications, improves reliability, and ensures uniform output across multi-site operations.
Centralized data collection also makes it easier to monitor trends and compare facility performance. It enables teams to identify deviations early, long before they affect finished product quality.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Digitizing workflows reduces the operational burden that comes with manual inspections, paper logs, and disconnected reporting. Automated processes minimize rework, product defects, and waste by ensuring that checks happen correctly and on time. Faster approvals and real-time access to records shorten cycle times for quality verification, supplier documentation, and production decisions.
By consolidating communication and documentation into a single system, teams avoid duplication of work and eliminate the delays caused by scanning, emailing, or manually compiling reports. This efficiency translates directly into lower labor costs and more streamlined operations.
Risk Mitigation
A modern quality management system strengthens risk control by detecting issues as soon as they occur. Real-time monitoring, alerts, and deviation tracking help teams respond quickly to prevent quality failures from escalating. Integrated corrective action tools support structured root cause analysis and ensure that preventive steps are fully documented and verified. Structured workflows enable teams to efficiently manage quality incidents by providing organized processes for investigating issues, implementing corrective actions, and tracking their effectiveness to prevent recurrence.
Together, these capabilities reduce the likelihood of recalls, regulatory non-compliance, and customer complaints. With improved visibility and faster response times, food companies can maintain tighter control over their processes and protect both their brand and consumers.
What Are the Key Features of Food Quality Management Software?
A modern Food QMS software centralizes the tools needed to maintain consistent quality, streamline compliance tasks, and support audit-ready operations.
The features below outline the core capabilities found in most leading platforms.

Digital Checklists and SOP Management
Digital checklists replace paper-based inspection forms and ensure operators follow standardized procedures. Automated prompts guide users through required steps, and version control ensures that only the latest SOPs and work instructions are used during production. Approval workflows maintain document integrity and help teams stay aligned with regulatory expectations.
Non-Conformance & CAPA
The CAPA module centralizes the way facilities capture, review, and resolve quality issues. Non-conformances can be logged immediately, routed to the appropriate team members, and investigated using built-in root cause analysis tools. Corrective and preventive actions are tracked to completion, ensuring long-term process improvements and full documentation for auditors.
Quality Testing and Laboratory Management
Food QMS solution supports both in-house testing and coordination with third-party laboratories. COAs, test results, and analytical data are stored alongside product and supplier records. Facilities can compare results to predetermined acceptance criteria, automate approval steps, and ensure that only materials meeting quality specifications move forward.
Supplier Quality Management
Supplier quality management consolidates vendor information and provides visibility into compliance, documentation status, and performance. This helps procurement and quality teams evaluate suppliers more accurately and maintain up-to-date approvals.
Where appropriate, the system supports:
- COA collection and verification
- Supplier audits and documentation tracking
- Ongoing risk scoring and performance monitoring
These tools help reduce vulnerabilities related to ingredient or packaging suppliers.
Batch Monitoring & Production Quality Control
Batch monitoring ensures that production processes remain within defined parameters. The software validates bills of materials and tracks critical quality attributes (CQAs) during manufacturing. It enables traceability by tracking raw materials through production batches to finished products, supporting quality control and compliance. In-process checks are captured digitally, offering real-time visibility into deviations and preventing quality failures before they reach the final product stage.
Document Control & Recordkeeping
Document control features maintain a centralized, secure repository for quality manuals, SOPs, training materials, and compliance records. Controlled access, revision histories, and approval workflows ensure that documents remain current and audit-ready. Digital archiving also simplifies retrieval during inspections or certification audits.
Audit Management
Audit management tools streamline the preparation, execution, and follow-up of internal and external audits. Schedules, checklists, findings, and corrective actions are organized within the system, reducing administrative work and maintaining continuous audit readiness. The software provides clear visibility into unresolved items and historical audit outcomes.
Traceability & Recall Management
Traceability capabilities track ingredients, batches, and finished goods across the supply chain, providing full traceability from raw materials to finished products. When issues arise, lot tracking enables rapid identification of affected materials, reducing recall impact. Immediate access to records is essential for rapid response during recalls and regulatory audits. The system can support mock recall exercises to verify readiness and ensure documentation aligns with regulatory and certification expectations.
Reporting & Analytics
Reporting tools consolidate data from inspections, tests, suppliers, and production activities into clear dashboards, providing actionable insights that inform process improvements and decision-making. These analytics help identify trends, recurring deviations, and opportunities for process optimization. KPI tracking supports continuous improvement initiatives and strengthens decision-making across departments.
Strengthen Traceability and Recall Preparedness
Customize the digital solution to
your exact business operations
What Are the Benefits of Using Food Quality Management Software?
Food quality management software strengthens operational control by standardizing how inspections, testing, and documentation are performed. This reduces variability across shifts and facilities, resulting in more consistent products and fewer quality failures.
Real-time data access improves decision-making by allowing teams to identify deviations immediately and act before issues escalate. Dashboards, alerts, and consolidated records give managers clear visibility into process performance without waiting for manual reports.
Stronger supplier oversight is another key advantage. Centralized COAs, audit reports, and performance metrics make it easier to evaluate vendor reliability and enforce purchasing requirements. This reduces the risk of receiving substandard ingredients or materials.
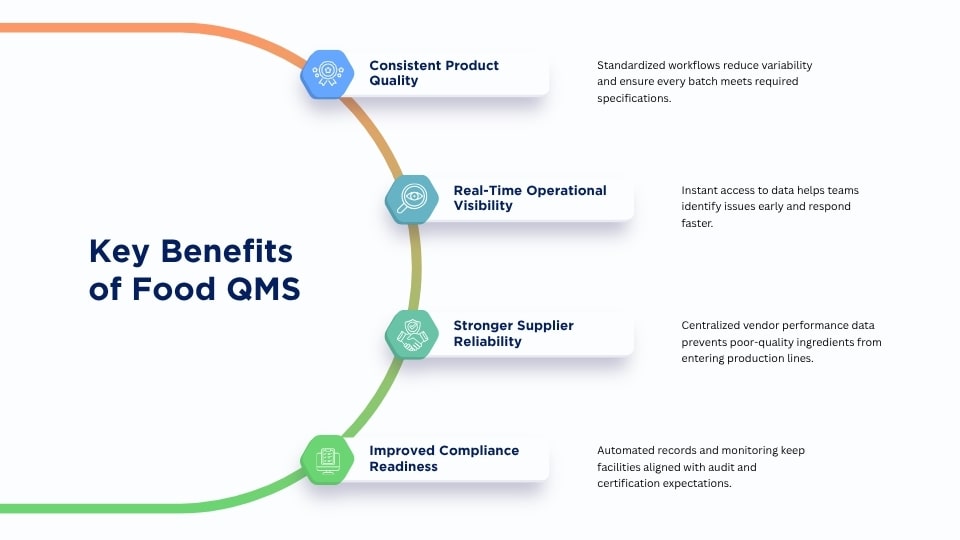
Automated compliance features help maintain alignment with regulatory and certification standards. The system ensures that records, SOPs, and monitoring activities are documented correctly and remain audit-ready at all times.
The platform also improves communication between departments by consolidating quality, production, and procurement data in one environment. This reduces misunderstandings, speeds up approvals, and enables coordinated responses to quality issues.
Finally, more controlled processes and faster issue resolution lead to higher customer satisfaction. With fewer defects, complaints, and disruptions, companies strengthen their brand reputation and deliver more reliable products to the market. Food quality management software is suitable for both large enterprises and mid-market organizations seeking scalable, flexible solutions to manage compliance and operational efficiency.
Who Needs Food Quality Management Software?
Food Manufacturers
Food manufacturers rely on quality management software to control production processes, monitor critical parameters, and maintain consistent product quality. The software helps manage in-process checks, testing data, and documentation required for regulatory and certification compliance.
Ingredient and Raw Material Suppliers
Ingredient and material suppliers use these systems to verify incoming materials, manage COAs, and maintain standardized specifications for products sold to manufacturers. QMS software also supports supplier audits, documentation tracking, and traceability expectations imposed by customers.
Co-Packers and Co-Manufacturers
Co-packers and co-manufacturers operate under tight customer requirements, making consistent recordkeeping and adherence to specifications essential. A centralized quality platform ensures that every run follows the correct formula, process, and packaging standards while maintaining complete documentation for clients and auditors.
Distributors and Logistics Providers
Distributors and logistics providers benefit from quality systems that monitor storage conditions, product handling, and traceability requirements. The software supports temperature monitoring documentation, lot tracking, and compliance with transportation regulations, reducing the risk of product damage or loss of control during food distribution.
Retail and Private-Label Brands
Retailers and private-label brands use quality management tools to oversee supplier performance, verify compliance, and ensure products meet brand specifications. The system centralizes testing results, audit findings, and supplier documentation, improving visibility across complex supply chains and reducing the risk of quality issues entering stores.
Commissaries and Central Kitchens
Commissaries and central kitchens depend on consistent workflows to produce large volumes of prepared foods. Quality management software standardizes recipes, monitors process controls, and verifies that food safety and quality checks are completed correctly for every batch. This supports operational efficiency and helps maintain uniform quality across multiple service sites.
Implementation Roadmap: How to Roll Out Quality Management Software?
Rolling out food quality management software requires a structured approach to ensure the system supports existing operations and strengthens compliance.
The following roadmap outlines a clear, controlled sequence for implementation.
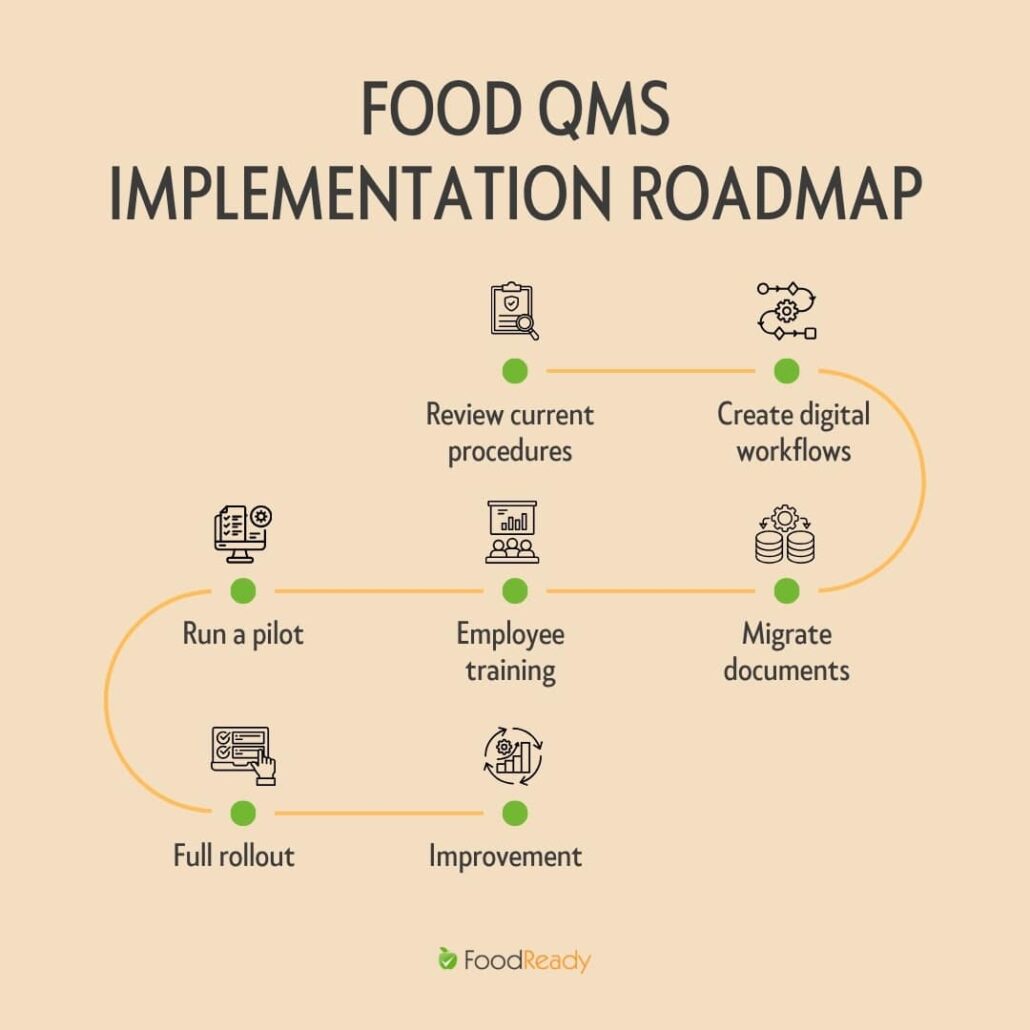
Assess Existing Quality Processes
Begin by reviewing current procedures, forms, testing practices, and documentation workflows. Identify gaps, redundant steps, and areas where manual processes create delays or inconsistencies. This assessment determines what needs to be digitized and where the new platform can provide the most value.
Map Workflows and Digitize Checklists
Once processes are documented, translate them into digital workflows. Convert daily inspections, quality checks, testing logs, and approval steps into electronic forms. At this stage, clarity and accuracy are essential. Digital checklists must reflect actual operations, certification requirements, and regulatory expectations.
Import Documentation and Supplier Files
Next, migrate core documents into the system. This typically includes:
- SOPs and work instructions
- Quality manuals and policies
- Supplier COAs, approvals, and audits
- Training materials and records
A clean document library ensures teams rely on the correct and most current information from the start.
Train Key Personnel
Before going live, provide targeted training to supervisors, quality staff, production leads, and anyone responsible for inputting or reviewing data. Focus on practical use: completing checklists, logging non-conformances, validating batches, and accessing documentation. Well-trained personnel reduce errors and accelerate adoption.
Pilot the Software
Launch a controlled pilot in one production area or with one process. The pilot is used to validate forms, assess user experience, and ensure the workflow matches real operations. Feedback from this phase should guide adjustments before expanding the system facility-wide.
Full Facility Rollout
After refining the system during the pilot, deploy it across all lines, shifts, and departments. Standardize onboarding materials and assign responsibilities for monitoring usage, resolving
Continuous Improvement and Audit Cycles
Once the system is fully operational, use its analytics, audit tools, and reporting features to monitor performance. Incorporate findings into improvement efforts. Regular review cycles ensure the software remains aligned with certification requirements, regulatory updates, and operational changes.
Security and Data Protection in Food Quality Management Software
In today’s food and beverage industry, safeguarding sensitive data is as critical as ensuring product quality. Food quality management software must be built on a foundation of robust security and data protection to maintain the integrity of quality records, supplier information, and compliance documentation. A modern quality management system (QMS) should employ advanced security measures such as data encryption, role-based access controls, and regular automated backups.
These features help prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and accidental losses. Risks that can have serious consequences for manufacturers.

Strong security protocols are not just best practices; they are essential for meeting regulatory compliance and industry standards, including those set by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI).
By implementing a secure QMS, food businesses can confidently manage audit management processes, demonstrate compliance during inspections, and protect their reputation in the marketplace. Ultimately, prioritizing security within your management software ensures that your food safety and quality data remain protected, supporting both operational excellence and customer trust.
Scalability and Flexibility for Growing Food Businesses
As food manufacturers expand, their QMS must keep pace with increasing complexity and evolving regulatory requirements. A scalable QMS is designed to grow alongside your business, accommodating more users, higher data volumes, and additional operational sites without sacrificing performance or compliance. Cloud-based management software offers the flexibility to add new modules, integrate with other systems, and adapt to changing business needs, whether you’re implementing new critical control points, updating hazard analysis protocols, or responding to new food safety regulations.
This adaptability is essential for maintaining consistent quality and operational efficiency as your business evolves. With a flexible QMS, food companies can streamline communication across teams, make data-driven decisions, and ensure compliance with standards like HACCP and SQF. By investing in scalable QMS software, food businesses can future-proof their operations, support continuous improvement, and maintain a competitive edge in a dynamic industry.
User Experience and Adoption Strategies
The success of any food QMS software hinges on user adoption. For food producers, choosing a QMS with an intuitive interface and streamlined workflows is key to ensuring that teams embrace the new system and use it effectively. A user-friendly platform minimizes training time, reduces human errors, and makes document control and supplier communication more efficient.
To drive successful implementation, organizations should consider phased rollouts, comprehensive training sessions, and ongoing support tailored to different user groups. Encouraging feedback from staff helps identify opportunities to further optimize the system and address any challenges early on. By prioritizing user experience and engagement, food businesses can maximize the benefits of their quality management software, improving food safety and quality, enhancing supplier relationships, and ensuring that quality processes are followed consistently across the organization.
Customer Support and Success: Ensuring Long-Term Value
Long-term success with quality management software depends on more than just the initial implementation. It requires ongoing support and a strong partnership with your QMS provider.
Food manufacturers should seek out management software vendors that offer comprehensive customer support, including technical assistance, training resources, and expert consulting. A dedicated customer success team can help your organization navigate regulatory requirements, such as FDA requirements, and adapt your QMS as your business needs evolve.
Responsive support minimizes downtime, resolves technical issues quickly, and ensures your team can focus on quality management and continuous improvement. By working closely with a knowledgeable provider, food businesses can stay ahead of industry changes, maintain compliance, and achieve a sustainable competitive advantage. Investing in customer support is an investment in the long-term value and effectiveness of your QMS software.
Measuring the Impact of QMS Software in the Supply Chain
For food producers, understanding the return on investment (ROI) of quality management software is essential for justifying the cost and driving ongoing improvement. By leveraging advanced analytics and reporting tools, organizations can track key performance indicators such as cost savings, reduced waste, improved product quality, and enhanced operational efficiency. These insights enable data-driven decisions that support optimal quality and profitability across the food and beverage industry.
A well-implemented QMS helps reduce errors, streamline processes, and ensure compliance, all of which contribute to measurable cost savings and increased customer satisfaction. Over time, these benefits translate into stronger customer loyalty, revenue growth, and a clear competitive advantage. By regularly reviewing ROI metrics and aligning your QMS with business goals, food manufacturers can ensure continuous improvement and maximize the long-term value of their management software investment.
Comparing Food Quality Management Software Solutions
1. FoodReady
Why use FoodReady?
FoodReady delivers an integrated AI platform for managing food safety operations and maintaining consistent quality across production, suppliers, and documentation workflows. Backed by artificial intelligence, the system centralizes records, supports hazard analysis, strengthens traceability, and automates key tasks to help facilities stay inspection-ready and meet both industry standards and customer expectations.
The software also integrates with enterprise resource planning tools and financial systems to provide unified operational visibility and help companies better serve customers.
FoodReady Features:
- Centralized Documentation: Create, revise, approve, and store all compliance-related records and operational materials in one secure environment.
- Compliance Oversight: Supports HACCP programs, ISO 22000, GFSI schemes, SQF standards, and FSMA requirements for digital, audit-ready evidence.
- Risk Assessment and Hazard Analysis: Identify potential hazards, assign preventive controls, and track mitigation steps through structured workflows.
- Inspection and Verification Coordination: Plan and execute internal checks, external evaluations, and certification reviews with digital scheduling and follow-up tools.
- Training and Competency Tracking: Manage employee qualifications, required courses, scheduled sessions, and completion records.
- Vendor Oversight: Monitor supplier information, evaluate risk and performance, and maintain documentation for approvals, certifications, and material verifications.
- Issue Resolution and Preventive Action: Capture deviations, trace root causes, and implement corrective or preventive steps to avoid recurrence.
- Reporting and Operational Analytics: Evaluate KPIs, spot trends in safety and production data, and gain visibility into areas requiring improvement.
- QuickBooks Integration: Sync financial information directly, reducing manual reconciliation and improving cross-department accuracy.
- Data Security and Access Control: Ensure sensitive operational and compliance data is safeguarded with permissions, encryption, and controlled access settings.
2. ETQ
Why use ETQ?
ETQ Reliance is the cloud-based QMS platform offered by ETQ, designed for regulated industries, including food and beverage. It supports advanced document control, change management, CAPA, and audit workflows to help companies maintain compliance and quality consistency.
ETQ Features:
- Maintaining Product Quality
- Auditing and Compliance
- Addresses Non-Conformance and Corrective Actions
3. ComplianceQuest
Why use ComplianceQuest?
ComplianceQuest provides a cloud-native QMS that helps food and beverage companies manage documentation, CAPA processes, supplier quality, and risk-based compliance activities. Its modular structure supports scalable deployment across diverse operations.
ComplianceQuest Features:
- Supplier Quality Management
- Risk Management and Regulatory Compliance
- Document Control and Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA)
4. MasterControl
Why use MasterControl?
MasterControl offers a robust QMS focused on compliance, CAPA, and document management. It is well-suited for food companies that require structured audit trails and strong process control in highly regulated environments.
MasterControl Features:
- Change Management and Communications Management
- Complaint Management and Compliance Management
- Quality Management
5. QT9 Quality Management
Why use QT9 Quality Management?
QT9 provides a cloud-based platform with integrated tools for document control, audits, inspections, and supplier monitoring. Its automated notifications and workflows simplify daily quality operations and help teams maintain consistent compliance.
QT9 Quality Management Features:
- Audit Management and Task Management
- Risk Management and Response Management
- Quality Assurance and Quality Management
6. Effivity
Why use Effivity?
Effivity delivers a digital platform for planning, implementing, and improving an organization’s QMS. It is designed to help companies simplify workflow management and maintain alignment with operational and regulatory expectations.
Effivity Features:
- Change Management and Communications Management
- Complaint Management and Compliance Management
- Workflow Management to Boost Productivity
7. SafetyChain
Why use SafetyChain?
SafetyChain provides a food-focused QMS that supports real-time monitoring, supplier oversight, and production quality controls. The platform is built to help plants streamline compliance and maintain visibility across daily operations.
SafetyChain Features:
- Supplier Management
- Food Safety and Quality Compliance
- Risk & Compliance Management
8. Intelex
Why use Intelex?
Intelex offers cloud-based QMS tools that help food businesses manage audits, documentation, and risk programs. Its focus on operational efficiency and customer satisfaction makes it a strong fit for multi-site and growing organizations.
Intelex Features:
- Simplify Operational and Change Management
- Decrease Cost of Quality
- Increase Customer Satisfaction
9. TrackWise Digital
Why use TrackWise Digital?
TrackWise Digital by Sparta Systems®, which is a Honeywell company, provides an enterprise-grade QMS with strong document control, CAPA, and supplier management capabilities. It supports food companies in maintaining compliance while improving visibility across quality operations.
TrackWise Digital Features:
- Document Control, Compliance Management, and Supplier Management
- Non-Conformance and Corrective Actions
- Audit Management and Risk Management
10. Plex Systems
Why use Plex Systems?
Plex Systems combines ERP and QMS functionality, offering integrated tools for document management, non-conformance tracking, and audits. Its unified platform makes it suitable for food businesses seeking both operational and quality oversight.
Plex Systems Features:
- Document Control and Compliance Management
- Supplier Management, Quality Inspections and Audits
- Non-Conformance and Corrective Actions
Future Trends in Food Quality Management Systems
The landscape of food quality management is shifting quickly as companies adopt smarter tools, automate processes, and respond to increasing regulatory pressure. Several key trends are shaping how modern QMS platforms operate today and what food businesses can expect in the coming years.
AI-Driven Process Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is moving from optional to foundational in quality operations. AI-enabled QMS platforms analyze inspection data, supplier records, and batch results to detect early warning signs long before they appear in finished products.
This predictive approach helps teams reduce quality drift, prioritize corrective actions, and strengthen preventive control programs.
Predictive and Real-Time Analytics
Analytics are evolving beyond static dashboards. Modern systems combine historical data, live inputs, and machine learning models to forecast deviations and pinpoint recurring issues.
A recent McKinsey industry study found that companies using real-time analytics improve operational responsiveness by up to 30%, highlighting the growing impact of data-driven decision-making in manufacturing environments.
Deeper System Integration Across the Tech Stack
Food manufacturers are increasingly seeking seamless connectivity between their QMS and broader operational systems. Integrations with ERP, MES, LIMS, and digital traceability tools eliminate siloed data and help teams maintain a unified operational view.
Key integration priorities include:
- Synchronizing production and quality data
- Automating material and supplier verification
- Linking batch records to traceability programs
- Connecting COAs directly to receiving workflows
These integrations reduce manual data entry and improve accuracy across the supply chain.
IoT and Automated Monitoring on the Plant Floor
Internet of Things (IoT) devices are now widely adopted in quality-critical environments. These devices provide continuous streams of validated data directly to the QMS, reducing reliance on manual checks and ensuring more accurate monitoring of CCPs, CQAs, and storage conditions.
Enhanced Digital Traceability and FSMA 204 Alignment
Traceability capabilities are becoming more robust as companies prepare for FSMA 204 and similar global regulations. Modern QMS platforms capture lot codes, transformation events, and supplier data automatically, enabling rapid retrieval during investigations or recalls.
Stronger ingredient-level visibility helps businesses reduce both recall impact and response time.
Cloud-Based and Mobile-First Architectures
Cloud-based QMS platforms are now the dominant deployment model. They offer faster updates, better scalability, and easier multi-site rollout. Mobile-first capabilities, such as on-floor checklist completion, barcode scanning, and instant document access, support more accurate data capture and faster task execution.
Automated Supplier Scoring and Risk Modeling
Supplier evaluation is increasingly moving toward automated risk modeling. Instead of manual spreadsheets, QMS platforms now score vendors based on COA results, audit outcomes, delivery consistency, and documentation status. This approach helps procurement and quality teams identify high-risk suppliers earlier and make more informed sourcing decisions.
FAQs
These trends show that food quality management systems are becoming more connected, predictive, and intelligence-driven. Companies that embrace these advancements will be better equipped to maintain consistent quality, reduce risk, and meet heightened regulatory expectations while operating more efficiently across their supply chain.
It is a digital system used to control, monitor, and document the processes that affect product quality, compliance, and consistency within a food operation.
It centralizes documentation, standardizes inspections, and supports requirements for HACCP, GMP, GFSI schemes (SQF, BRCGS, FSSC 22000), and FSMA.
Food safety prevents hazards that can cause illness, while quality management ensures products meet defined specifications, sensory attributes, and consumer expectations.
Manufacturers, co-packers, suppliers, distributors, central kitchens, and private-label brands benefit from standardized quality workflows and improved traceability.
Yes. By enforcing consistent checks, monitoring critical parameters, and providing live monitoring, the software reduces variation and prevents defects from reaching customers.
Key features include digital checklists, CAPA management, supplier quality oversight, document control, traceability, audit tools, and reporting dashboards.
Most platforms include lot tracking, backward and forward traceability, and mock recall capabilities to speed up investigations and limit risk.
Many solutions offer APIs or built-in integrations for ERP, MES, LIMS, inventory, or finance tools to streamline data sharing and reduce manual entry.
Timelines vary, but most organizations complete setup in several weeks to a few months, depending on process complexity and data migration needs.
Yes. Centralized controls, standardized forms, and unified reporting make it ideal for companies operating multiple facilities or co-manufacturing locations.
It stores COAs, audits, approvals, and performance data, allowing teams to evaluate supplier reliability and maintain compliance with purchasing requirements.
Improved consistency, reduced defects, faster decision-making, automated compliance workflows, stronger supplier oversight, and better customer satisfaction.








